|
|

Artur Silva

Josť Cavaleiro |
LAB PRESENTATION
The Organic Chemistry and Natural Products Research Group at the Aveiro University
The Aveiro Organic Chemistry and Natural Products Group is performing its research activities in the Department of Chemistry of the local University. Such activities are centered on the development of new synthetic methodologies leading to biologically significant new products. The latter include tetrapyrrolic macrocycles and of some of their metal complexes, polyphenolic compounds, quinolone and acridone derivatives, and cyclohexane derivatives bearing several stereocenters. Regio- and enantioselective organocatalytic conjugated additions, diastereoselective domino multicomponent reactions, homogeneous and heterogeneous catalytic transformations, using polyoxotungstates and metalloporphyrins as catalysts, and the use of microwave irradiation in the chemical transformations under study are also targets in the mentioned studies. In interdisciplinary approaches and looking for potential applications concerned with the valorisation of the new compounds, the following working lines are considered: i) use of porphyrin derivatives, as photosensitizers, in cancer treatment and in the photoinactivation of microorganisms; ii) use of nitrogen and oxygen heterocyclic compounds as anti-inflammatory and antitumour agents and as food additives.
Prof. José Cavaleiro was the founder of this research group in the University of Aveiro and is full professor of Organic Chemistry since 1986. He is the main responsible for the tetrapyrrolic macrocycles research line. Prof. Artur Silva was a student at the University of Aveiro, PhD student of Prof. José Cavaleiro and is full professor of Organic Chemistry since 2001. He is the main responsible for the nitrogen and oxygen heterocyclic (mainly polyphenols) compounds research line. Both research lines are also interested in the catalytic transformations, using organocatalysts or polyoxotungstates and metalloporphyrins as catalysts.
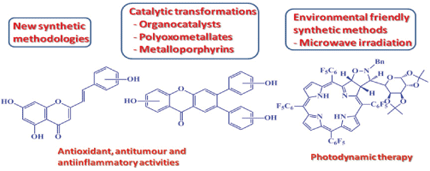
In the last decade, we have a long track in the development of new synthetic methods for several polyphenolic compounds (e.g. 2- and 3-styrylchromones, xanthones, flavones) and in the preparation of several new derivatives to be assessed as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agents. These studies showed that polyhydroxy-2-styrylchromones exhibited potent xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity, protective effects against the hepatotoxicity mediated by pro-oxidant agents, and important antioxidant properties. We also demonstrated that active antioxidant 2-styrylchromones are also potent inhibitors of LOX and COX enzymes. It was also demonstrated that polyhydroxy-2,3-diarylxanthones present an outstanding ROS and RNS scavenging properties, considering the nanomolar to micromolar range of the IC50 values found. The xanthones with two catechol rings were the most potent scavengers of all tested ROS and RNS. These antioxidants are also superior to quercetin in protecting human skin keratinocytes against tert-butylhydroperoxide induced oxidative stress and also in the inhibition of Cu2+-induced lipid peroxidation of human LDL.
The transformation of some of the referred polyphenolic compounds throughout cycloaddition and cross-coupling reactions and also the establishment of new synthetic methods of nitrogen heterocyclic compounds, such as pyrazoles, triazoles, acridones and 4-quinolones, due to their potential important biological activities, have also been one of our main target of work.
The design of complex organic molecules with multiple stereogenic centres is a continuing challenge at the forefront of synthetic chemistry. One approach to this challenge involves the development of catalytic domino, cascade or tandem multicomponent reactions. For a long time, asymmetric organocatalysis, in which small chiral organic molecules act as active species, was predominated in the field of organic synthesis because are metal free, usually nontoxic and environmentally friendly. Recently, we have also developed novel diastereoselective domino multicomponent reactions under phase-transfer conditions to construct cyclohexane derivatives with five new stereocenters, which contain hydroxy, nitro and ketone functional groups and a quaternary carbon atom. Structures that include a stereogenic quaternary carbon are one of the most demanding topics in the synthesis of natural products and pharmaceutical agents.
During the last two decades, porphyrins, corroles and phthalocyanines are being explored as important tools for new applications, such as catalysts, advanced biomimetic models for photosynthesis, new electronic materials, sensors and as drugs. We have been focused on the synthesis and transformation of tetrapyrrolic macrocycles into new derivatives with improved features that may turn them possible candidates to be used in different areas. These studies included: i) functionalization of porphyrins and corroles through cycloaddition reactions, reactions involving transition metal catalysts and nucleophilic aromatic substitution; ii) development of new porphyrin derivatives and analogues with adequate structural characteristics to be used as photosensitizers in PDT, to be evaluated for their bactericidal, fungicidal, virucidal and antitumoral activities; iii) preparation and characterization of novel homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts based on iron or manganese substituted polyoxotungstates and metalloporphyrins and analogues, including the evaluation of their catalytic performance in the oxidation of aromatic hydrocarbons, aromatic heterocycles and terpenes; iv) preparation of phthalocyanines and calix[4]pyrrole derivatives and their use as anion sensors.
Our synthetic work aims to establish novel synthetic methods, using environmental friendly synthetic approaches, so we have been developing new methods using microwave irradiation as the energy source, in solvent free-conditions or under a reduced volume of organic solvents.
These pioneering studies on polyphenolic compounds and tetrapyrrolic macrocycles demonstrate that new bioactive agents with a desired structural profile can be obtained.
2-Styrylchromones an useful synthetic synthon and a source of potential drugs
The inflammatory process is a complex physiological response, which involves an increase in vascular permeability as well as release of lipid-derived autacoids, but also an overproduction of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (ROS and RNS). If these reactive species overcome host defense systems, exacerbated damage in inflammatory sites may occurred, contributing to chronic diseases. Therefore, in order to control these diseases, anti-inflammatory substances need to be used that should also possess antioxidant properties. Polyphenolic compounds have drawn a great deal of attention compared to other natural products mainly due to their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anticarcinogenic properties. The similarity of 2-styrylchromones with flavones and some of their know biological activity led us to develop new synthetic methods for this type of compounds and to design some novel molecules which have present important antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-norovirus activities while a certain derivatives was identified as a selective proliferation inhibitor of human tumor (MCF-7 and NCI-H460) cell lines.
2-Styrylchromones were also the starting material, throughout cross-coupling reactions, for the development of a novel group of polyphenolic compounds, polyhydroxy-2,3-diarylxanthones, for which we have also already demonstrated potent antioxidant activities. Some of the biological applications of these compounds were the subject of a European patent application.
All this trans-disciplinary work was developed in collaboration with some Portuguese (Eduarda Fernandes and M. São José Nascimento, Pharmacy Faculty of Porto) and French (René Santus, Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle de Paris, and Patrice Morliére, Laboratoire de Biochimie, CHU Amiens) research groups.
Cationic and glycoconjugate porphyrin derivatives
Structural features are required for a new porphyrin derivative to be considered as a photosensitizer (PS) in photodynamic therapy (PDT). And for that each new PS must exhibit adequate amphiphilic properties. And these have been big synthetic challenges. In such way dihydro-type or tetrahydro-type porphyrins (respectively chlorins and bacteriochlorins) as well as certain cationic and glycoconjugate derivatives have been targets for several research groups.
We have been able to establish that certain porphyrin macrocycles can act as dienophiles or dipolarophiles in Diels-Alder cycloadditions; in such way novel chlorin or bacteriochlorin types can become available. The formation of glycoconjugates can also be obtained in such way. It was also demonstrated that novel cationic derivatives can become available by using our reported methodology. In collaboration with other groups the new products have been assessed as photosensitizing agents in PDT or in the photoinactivation of microorganisms. In particular the action against antibiotic resistant bacteria, mainly the Gram (-) ones, is of great significance. It is also possible to photoinactivate microorganisms present in water samples, including sewage ones. Such potential applications have been patented.
The biological assesssment work has been carried out in collaboration with colleagues from other areas (Biology departments of the Universities of Aveiro, Lisbon, Padova, Humboldt, Autonoma-Madrid and from Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle de Paris, and Laboratoire de Biochimie, CHU Amiens).
_____________________________________________________
Contact
Artur Silva and José Cavaleiro
Department of Chemistry
University of Aveiro
3810-193 Aveiro
Portugal
Email: artur.silva@ua.pt and jcavaleiro@ua.pt
Website: http://www.ua.pt/dq/PageText.aspx?id=6340
_____________________________________________________
Selected recent publications
- 1,3-Dioxopyrrolo[3,4-b]porphyrins: Synthesis and Chemistry, C. M. B. Carvalho, M. G. P. M. S. Neves, A. C. Tomé, F. A. A. Paz, A. M. S. Silva and J. A. S. Cavaleiro, Org. Lett., 2011, 13, 130-133.
- 2,3-Diarylxanthones as strong scavengers of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species: A structure-activity relationship study, C. M. M. Santos, M. Freitas, D. Ribeiro, A. Gomes, A. M. S. Silva, J. A. S. Cavaleiro, E. Fernandes, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2010, 18, 6776-6784.
- Diporphyrinylamines: Synthesis and Electrochemistry, A. M. V. M. Pereira, M. G. P. M. S. Neves, J. A. S. Cavaleiro, C. Jeandon, J.-P. Gisselbrecht, S. Choua and R. Ruppert, Org. Lett., 2011, 13, 4742-4745.
- Functional Cationic Nanomagnet-Porphyrin Hybrids for the Photoinactivation of Microorganisms, C. Carvalho, E. Alves, L. Costa, J. P. C. Tomé, M. A. F. Faustino, M. G. P. M. S. Neves, A. C. Tomé, J. A. S. Cavaleiro, Â. Almeida, Â. Cunha, Z. Lin, J. Rocha, ACS Nano, 2010, 4, 7133-7140.
- Highly Enantioselective and Regioselective Conjugate Addition of Nitromethane top 1,5-Diarylpenta-2,4-dien-1-ones Using Bifunctionla Cinchona Organocatalysts, C. G. Oliva, A. M. S. Silva, F. A. A. Paz, J. A. S. Cavaleiro, Synlett, 2010, 1123-1127.
- New Synthesis of (Z)- and (E)-3-Styryl-4-quinolones, Raquel S. G. R. Seixas, Artur M. S. Silva, José A. S. Cavaleiro, Synlett, 2010, 2257-2262.
- New Synthesis of 2,3-Diarylacridin-9(10H)-ones and (E)-2-Phenyl-4-styrylfuro[3,2-c]quinolines, V. L. M. Silva, A. M. S. Silva, J. A. S. Cavaleiro, Synlett, 2010, 2565-2570.
Oxidation of styrene and of some derivatives with H2O2 catalyzed by novel imidazolium-containing manganese porphyrins: A mechanistic and thermodynamic interpretation”, R. De Paula, M. M. Q. Simões, M. G. P. M. S. Neves and J. A. S. Cavaleiro, J. Mol. Catalysis A: Chemical, 2011, 345, 1-11.
- Photodynamic Antimicrobial Chemotherapy in Aquaculture: Photoinactivation Studies of Vibrio fischeri, E. Alves, M. A. F. Faustino, J. P. C. Tomé, M. G. P. M. S. Neves, A. C. Tomé, J. A. S. Cavaleiro, A. Cunha, N. C. M. Gomes and A. Almeida, PloS One, 2011, 6, e20970-e20978.
- Reactivity of 3-Iodo-4-quinolones in Heck Reactions: Synthesis of Novel (E)-3-Styryl-4-quinolones, A. I. S. Almeida, A. M. S. Silva, J. A. S. Cavaleiro, Synlett, 2010, 462-466.
- Structure-activity relationship in hydroxy-2,3-diarylxanthone antioxidants. Fast kinetic spectroscopy as a tool to evaluate the potential for antioxidant activity in biological systems, C. M. M. Santos, A. M. S. Silva, P. Filipe, R. Santus, L. K. Patterson, J.-C. Mazière, J. A. S. Cavaleiro, P. Morlière, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2011, 9, 3965-3974.
- Synthesis and characterization of new porphyrin/4-quinolone conjugates”, A. T. P. C. Gomes, A. C. Cunha, M. R. M. Domingues, M. G. P. M. S. Neves, A. C. Tomé, A. M. S. Silva, F. C. Santos, M. C. B. V. Souza, V. F. Ferreira and J. A. S. Cavaleiro, Tetrahedron, 2011, 67, 7336-7342.
|
|

Editor
Gabriele Costantino
Univ. of Parma, IT
Editorial Committee
Erden Banoglu
Gazi Univ., TR
Lucija Peterlin Masic
Univ. of Ljubljana, SLO
Leonardo Scapozza
Univ. of Geneve, CH
Wolfgang Sippl
Univ. Halle-Wittenberg, DE
Sarah Skerratt
Pfizer, Sandwich, UK

Executive Committee
Uli Stilz President
Gerhard F. Ecker Past Pres.
Koen Augustyns Secretary
Rasmus P. Clausen Treasurer
Hein Coolen Member
Gabriele Costantino Member
Phil Jones Member

|









